
Emerald Ash borer (EAB) is confirmed to infest in many areas of the U.S. Emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis) is an exotic beetle that was discovered in southeastern Michigan near Detroit in 2002. EAB adult beetles nibble on ash foliage but cause little damage. The beetle larvae (immature stage) feed on the inner bark of ash trees, disrupting the tree’s ability to transport water and nutrients.
EAB is native to Asia and probably arrived in the U.S. around 1990 in wood packing material. Over 100 millions of ash trees have been lost in over 18 states, and in Ontario and Quebec, Canada. The cost to municipalities, property owners, nursery operators and forest products industries is in the tens of millions of dollars in the treatment and tree removal costs or lost logging production. This pest continues to spread.
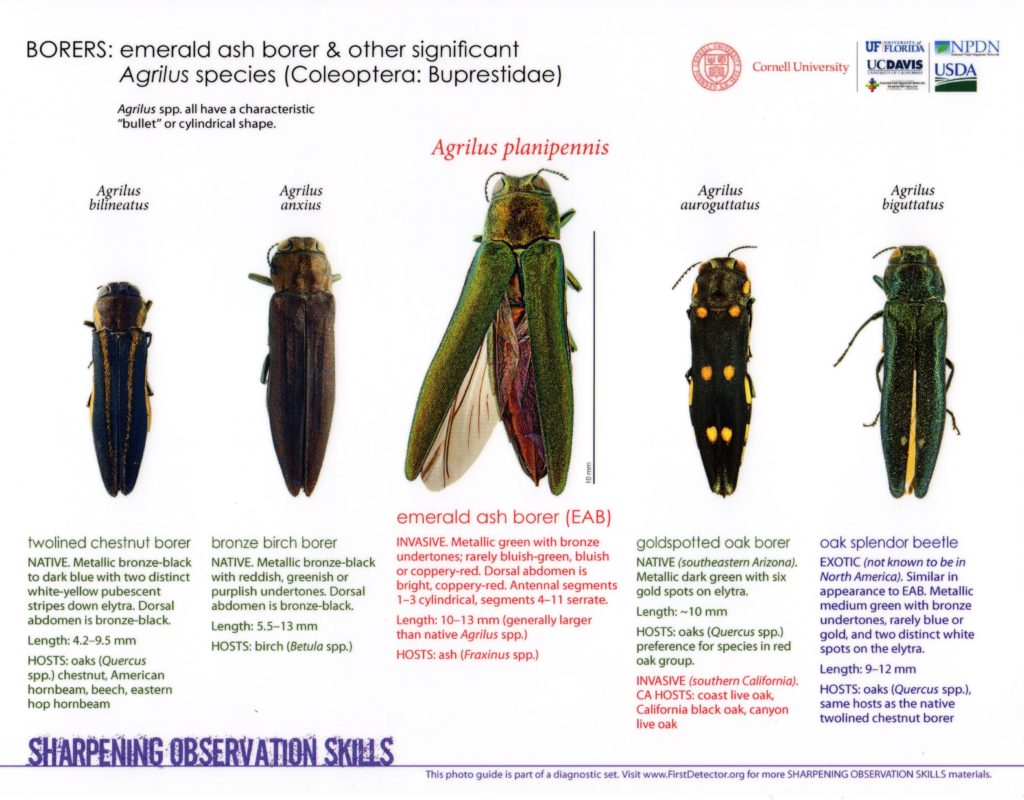
EAB threatens the entire North American Fraxinus genus, unlike past invasive tree pests, which have threatened only one or a few species within a genus. Green ash (F. pennsylvania), black ash (F. nigra) and white ash (F. americana) trees are preferred hosts. Blue ash (F.
quadrangulata) displays temporary resistance to the EAB larvae but are eventually killed as well.
EAB is a very destructive insect pest in North America in terms of both the number of trees affected and the economic losses associated with the treatment and removal costs.
According to University of Tennessee plant scientists, property owners should: 1. Don’t transport firewood, even within the state. 2. Use firewood only from local sources, or purchase firewood that is certified (labelled) to be free of pests. 3. If you have moved firewood, burn all of it before leaving your campsite. 4. Watch for signs of infestation in your ash trees.
Finally, if you suspect an ash tree to be infested with EAB, call your county or city Extension office or contact a state certified arborist.
EMERALD ASH BORER

 Posted in
Posted in 
